
- General Lab Safety 5 modules
- Solutions and Buffers 27 experiments
- Biochemistry of Carbohydrates 18 experiments
- Biochemistry of Amino Acids & Proteins 17 experiments
- Biochemistry of Enzymes 23 experiments
- Biochemistry of Lipids 15 experiments
- Proximate Analysis 11 experiments
Purchase Information
Price: 600/- PKR
Edition: 2023-2024 (3rd edition)
ISBN: 978-627-7502-04-1 (Print)
Published by Dr. Muhammad Ali
Five (05) modules of lab safety and One hundred and eleven (111) full-length experiments are included.
© Copyright 2023. All rights reserved by Dr. Muhammad Ali
Contact us for purchase and online ordering:
0320-7177763
[email protected]
Video lectures of almost all the experiments will be uploaded sequentially.

Experiment 3.1- Molisch’s test for the identification of carbohydrates
1- Sucrose shows red color (tube A). 2- The appearance of deep blue color will indicate the presence of polysaccharides (tube B). 3- Glucose shows yellowish color (tube C).

Experiment 3.2- Iodine test for the identification of polysaccharide
Deep blue coloration that disappear on heating and appears on cooling shows polysaccharises
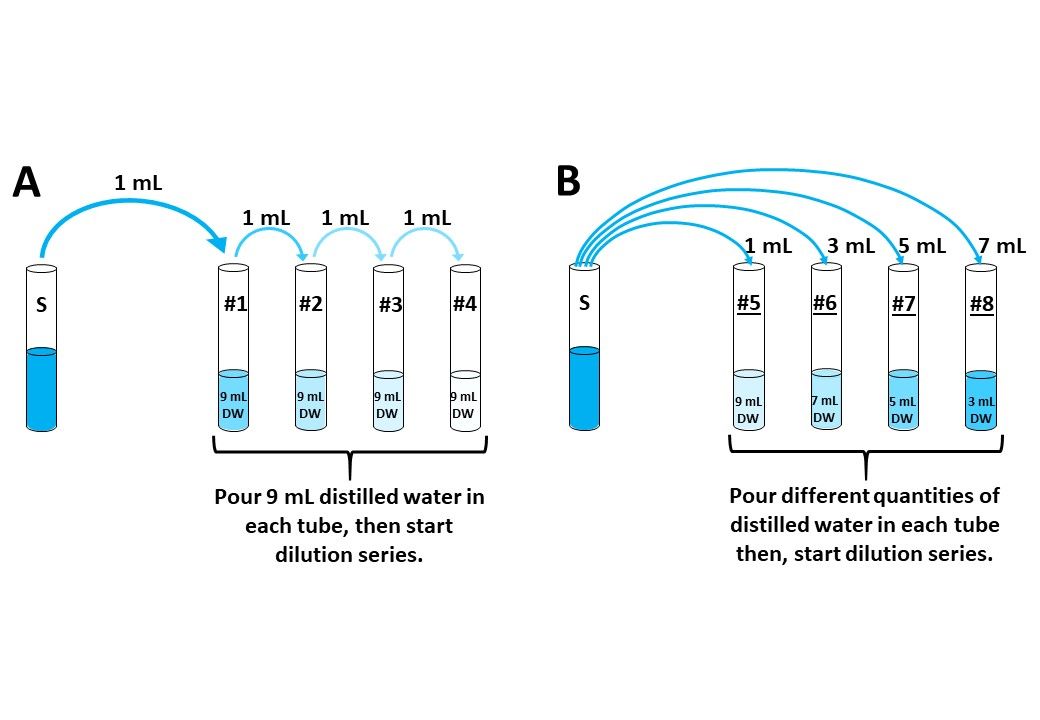
Experiment 2.13- Prepare serial and parallel dilutions of 1 M CuSO4 solution.
Serial dilutions are used to find IC_50 values of drugs. Parallel dilutions can be used to make a standard for the calibration curve. The dilution series can also be used for spiking.
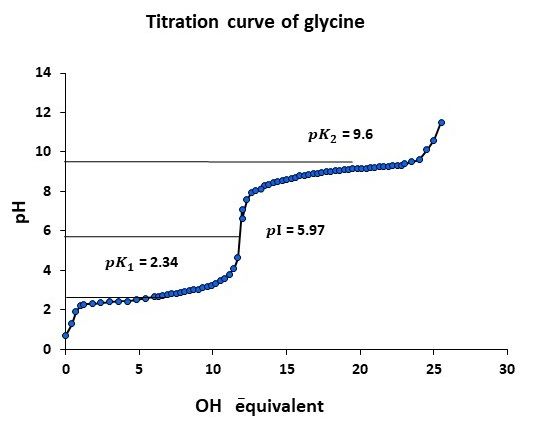
Experiment 4.2- Draw titration curve of glycine and mark pI and 〖pK〗_(a )values.
Glycine has pKa1, pKa2, and pI values of 2.34, 9.6, and 5.97 respectively.
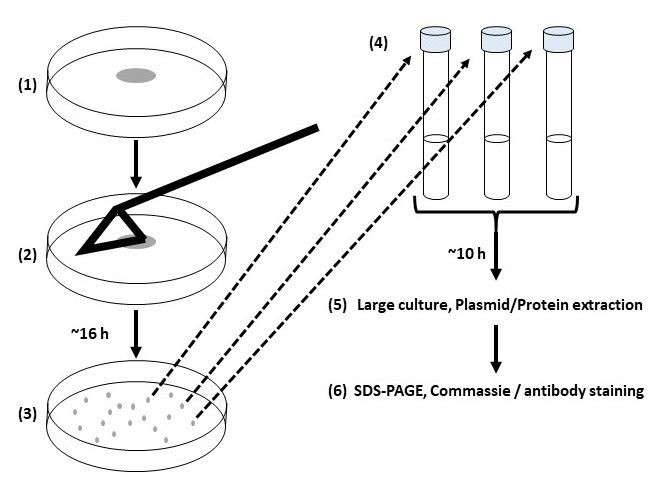
Experiment 5.3- Transformation of plasmid vectors in competent cells (E. coli)
Transformed bacteria are used in enzymology for the production of enzymes. Moreover, the transformation is used to multiply copies of plasmids containing genes of our interest.
Contents of EBB Series-I (Blue)
1.1 Instructions for practical work in the laboratory. 1
1.2 Understanding the precautions of lab safety. 1
1.3 First aid in the laboratory. 1
1.4 First aid kit in the laboratory. 2
1.5 Personal and general lab safety. 2
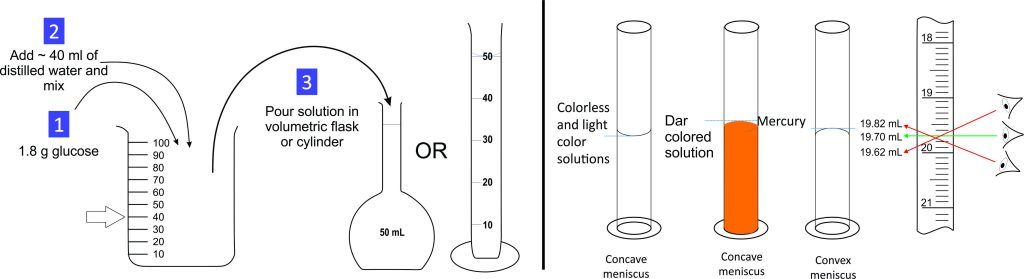
Experiment 2.1- Prepare 50 mL of 0.2 molar (0.2 m) glucose solution. 7
Experiment 2.2- Prepare 50 g of 0.5 molal NaCl solution. 8
Experiment 2.3- Calculate molarity of concentrated sulfuric acid of 95% purity (ρ =1.84 g/mL). 8
Experiment 2.5- How will you make 500 mL of 0.601 m solution of HNO3. 10
Experiment 2.6- How will you prepare 500 mL of 1 m H3PO4 solution when it is 85.0% pure. 10
Experiment 2.7- Prepare 150 mL of 2% (w/v) NaCl solution. 11
Experiment 2.8- What is w/v % of 1 m NaCl solution?. 12
Experiment 2.10- Prepare 80 mL of 70% (v/v) ethanol (C2H5 -OH) solution. 13
Experiment 2.11- Prepare 200 mL of 200-ppm CaCl2 solution. 13
Experiment 2.12- Prepare 100 mL of 20 ppb CaCl2 solution from its 100 ppm stock solution. 14
Experiment 2.13- A certain solution has 1 × 10-5 m CaCl2. What is the concentration in ppm?. 14
Experiment 2.16- Prepare serial and parallel dilutions of 1 m CuSO4 solution. 16
Experiment 2.18- Prepare 200 mL of 0.5 m Tris buffer and adjust pH to 6.8 (pKa of Tris = 8.1). 18
Experiment 2.19- Prepare 200 mL of 0.5 m EDTA solution and adjust pH to 8.0. 19
Experiment 2.20- Prepare 50 mL of 10 % SDS solution. 19
Experiment 2.22- Prepare 1 liter of 0.2 m phosphate buffer of 7.3 pH. 21
Experiment 2.23- Prepare acetate and phosphate buffers of different pH. 22
Experiment 2.24- Prepare 100 mL of lysis buffer for protein extraction. 23
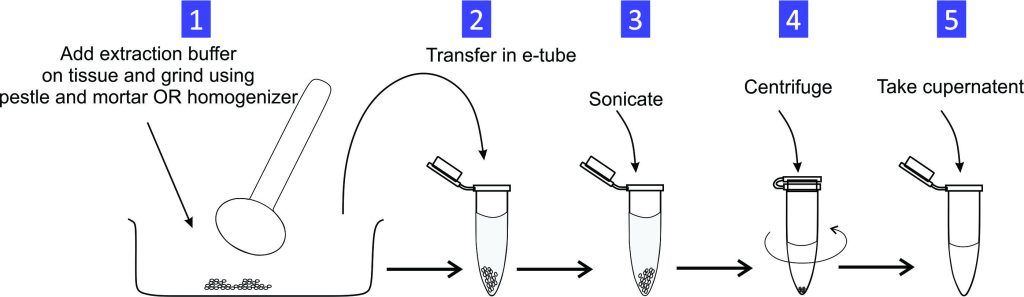
Experiment 2.25- Prepare 40 mL of DNA extraction buffer. 24
Experiment 2.26- Demonstration about diffusion and dialysis. 25
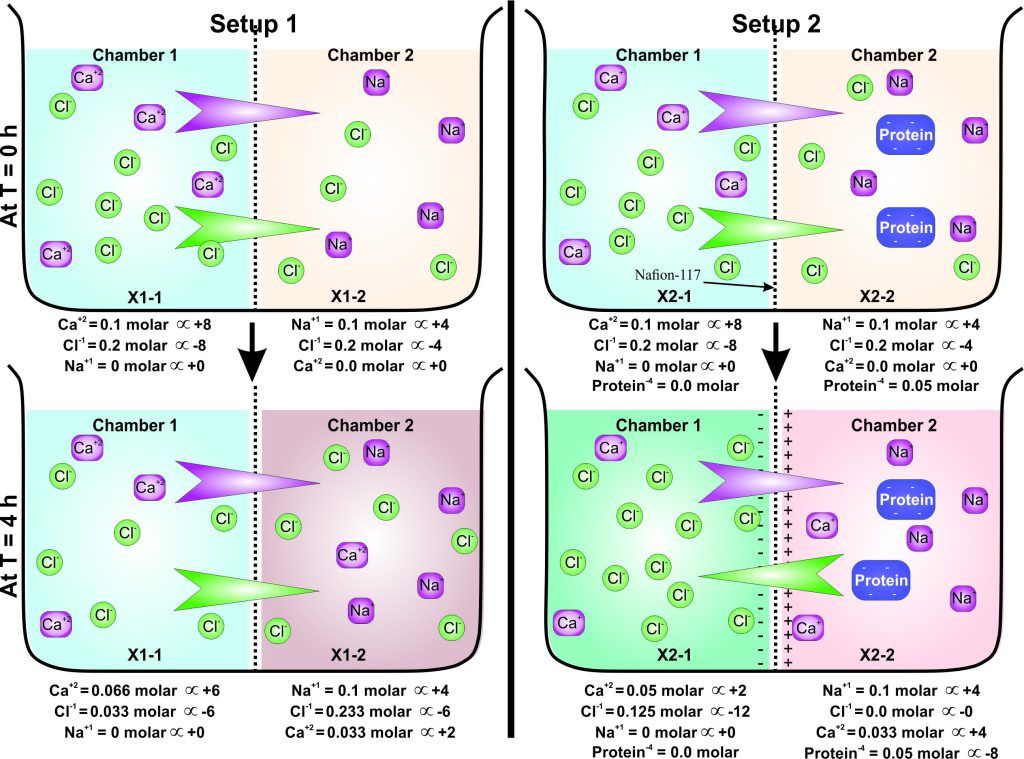
Experiment 2.27- Donnan’s equilibrium and osmosis. 26
Exam questions for solutions, buffers, and pH.. 27
Experiment 3.1- Molisch’s test for the identification of carbohydrates. 37
Experiment 3.2- Iodine test for the identification of polysaccharide. 38
Experiment 3.3- Fehling’s test for the identification of reducing sugars. 38
Experiment 3.4- Benedict’s test for the identification of reducing sugar. 39
Experiment 3.5- Barfoed’s test for the identification of monosaccharides. 40
Experiment 3.6- Osazone test for aldo and keto group of sugar. 41
Experiment 3.7- Seliwanoff’s test for the identification of keto group. 42
Experiment 3.8- Bial’s test for the identification of pentoses. 42
Experiment 3.9- Quantitation of glucose by using DNS reagent. 43
Experiment 3.10- Estimation of optical activity of D-glucose by polarimetry. 44
Experiment 3.11- Quantitation of glucose by polarimeter. 45
Experiment 3.12- Estimation of blood glucose by glucose oxidase method. 46
Experiment 3.13- Chromatographic separation of monosaccharides. 48
Experiment 3.14- HCl-mediated hydrolysis of sucrose. 50
Experiment 3.15- HCl-mediated hydrolyses of starch. 50
Experiment 3.16- Rapid extraction of glycogen from fresh mouse liver. 51
Experiment 3.17- HCl-mediated hydrolysis of glycogen obtained from mouse liver. 52
Experiment 3.18- Glucose tolerance test (GTT) for the diagnosis of diabetes. 53
Experiment 4.1- Perform different qualitative test for the identification of amino acids. 56
Experiment 4.2- Draw titration curve of glycine and mark pI and values. 56
Experiment 4.3- Hydrolysis of protein from dried plant tissues. 57
Experiment 4.4- Qualitative test for amino acids obtained by the hydrolysis of proteins. 58
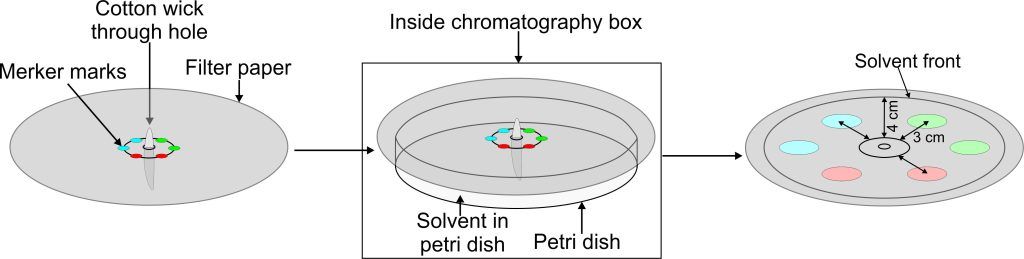
Experiment 4.5- Circular chromatography. 59
Experiment 4.6- Fractionation of color pigments of berseem.. 60
Experiment 4.7- Extraction of total proteins from leaves of rice plant. 61
Experiment 4.8- How will you extract total proteins from animal tissues?. 62
Experiment 4.9- Separation of a nuclear and cytosolic fraction of proteins. 63
Experiment 4.10- Protein quantitation by UV spectroscopy. 63
Experiment 4.11- Estimation of total serum proteins by the Biuret method. 64
Experiment 4.12- Estimation of total serum proteins by Lowry assay. 66
Experiment 4.13- Quantitation of proteins by BCA assay. 67
Experiment 4.14- Bradford assay (dye binding assay) for protein quantitation. 68
Experiment 4.15- Size exclusion (column) chromatography for the separation of proteins. 69
Experiment 4.16- Determination of molecular weight of proteins by SDS-PAGE. 70
Experiment 4.17- Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA). 71
Experiment 5.1- Prepare nutrient LB-media and LB-agar plates for bacterial culture. 76
Experiment 5.2- Isolate pure colonies of E. coli (DH10-α) from its culture. 76
Experiment 5.3- Transformation of plasmid vectors in competent cells (E. coli). 77
Experiment 5.4- Purification of GST-tagged enzyme from bacterial culture. 78
Experiment 5.5- Microbial technology for the production of lactase (β-Galactosidase). 80
Experiment 5.6- Isolation of enzymes by ammonium sulphate precipitation. 82
Experiment 5.7- Purification of enzymes by ion exchange. 84
Experiment 5.8- Produce cellulase enzyme using Bacilus substilus (AU-1). 85
Experiment 5.9- Hydrolysis of starch using amylase enzyme. 86
Experiment 5.10- Effect of pH on the enzymatic activity of salivary amylase. 86
Experiment 5.11- Effect of temperature on the reaction rate of α-amylase. 87
Experiment 5.12- Effect of cofactors and metal ions on enzyme (lactase) activity. 88
Experiment 5.13- Effect of inhibitors on enzyme activity. 89
Experiment 5.14- Find optimum temperature for enzymatic activity of trypsin. 90
Experiment 5.15- Determine optimum pH for trypsin activity (calorimetric). 91
Experiment 5.16- Determine the optimum pH of chymotrypsin calorimetrically. 93
Experiment 5.17- Determine substrate specificity of trypsin and chymotrypsin. 95
Experiment 5.18- Determine the optimum pH for the activity of pepsin. 96
Experiment 5.19- Find Km value of pepsin enzyme. 97
Experiment 5.20- Effect of temperature on the activity of catalase enzyme. 98
Experiment 5.21- Thermodynamic studies and kinetic models of enzymes. 98
Experiment 5.22- Determination of thermo-stability and half life. 100
Experiment 5.23- Immobilization of enzymes using different supports and techniques. 101
Experiment 5.24- Characterization of free & immobilized enzymes. 102
Experiment 6.1- Solubility test of lipids in water and organic solvent. 106
Experiment 6.2- Grease spot test for lipids. 106
Experiment 6.3- Test for the identification of free fatty acids in corn oil 107
Experiment 6.4- Emulsification of lipids by using bile salt. 107
Experiment 6.5- Saponification value of corn oil (lipid). 107
Experiment 6.6- Tests for the unsaturation of fatty acids. 109
Experiment 6.7- Extraction of total lipids from mouse brain tissue. 110
Experiment 6.8- Fractionation of lipids by using 2-dimensional TLC. 110
Experiment 6.9- Isolation of free fatty acids from soap. 112
Experiment 6.10- Acrolein test for glycerol identification. 112
Experiment 6.11- Dichromate test for the identification of glycerol 113
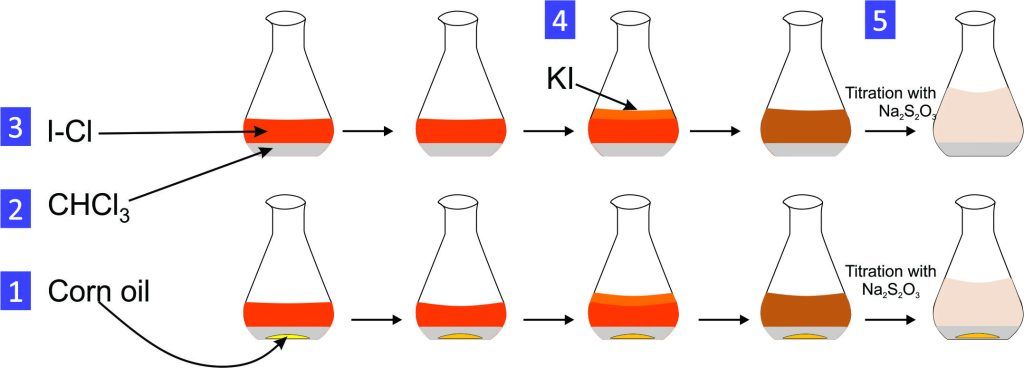
Experiment 6.12- Determination of iodine number of cooking oil 113
Experiment 6.13- Liberman-Burchard test for the quantitation of cholesterol 114
Experiment 6.14- Salkowski’s test for cholesterol identification. 115
Experiment 6.15- Colorimetric determination of phospholipids (ammonium ferrothiocyanate method). 117
Experiment 7.1- Determination of moisture contents of raisin. 120
Experiment 7.2- Determination of ash content of cabbage. 121
Experiment 7.3- Extraction and qualitative analysis of soluble sugars. 122
Experiment 7.4- Extraction and qualitative analysis of starch. 123
Experiment 7.5- Protein quantification by Kjeldahl method. 124
Experiment 7.6- Estimation of fat contents in almond. 125
Experiment 7.7- Estimation of fat by chloroform–methanol procedure (Folch extraction). 127
Experiment 7.8- Extraction of oil by Soxhlet method. 128
Experiment 7.9- Estimation of vitamin C (Ascorbic acid) in orange samples (mg /g of fruit). 129
Experiment 7.10- Colorimetric estimation of vitamin A with trichloroacetic acid. 130
Experiment 7.11- Estimation of lactose and casein in milk. 131
7.1- Reagents for Biochemistry and Biotechnology lab. 133
7.2- Composition for Tris-glycine SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). 135

Comments are closed.